Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Yuki; Murakami, Hiroyuki*; Shimaoka, Takehiro*; Tsubota, Masakatsu*; Kaneko, Junichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 834, p.218 - 222, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)Shimaoka, Takehiro*; Kaneko, Junichi*; Sato, Yuki; Tsubota, Masakatsu*; Shimmyo, Hiroaki*; Chayahara, Akiyoshi*; Watanabe, Hideyuki*; Umezawa, Hitoshi*; Mokuno, Yoshiaki*
Physica Status Solidi (A), 213(10), p.2629 - 2633, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Yuki; Murakami, Hiroyuki*; Shimaoka, Takehiro*; Tsubota, Masakatsu*; Kaneko, Junichi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(4), p.046401_1 - 046401_5, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.99(Physics, Applied)We investigated the performance of a charged particle detector fabricated using single-crystal diamond grown by chemical vapor deposition. The detector was able to identify four different  Am
Am  -particle energies (5.389, 5.443, 5.486, and 5.545 MeV) because of its superior intrinsic energy resolution of
-particle energies (5.389, 5.443, 5.486, and 5.545 MeV) because of its superior intrinsic energy resolution of  0.4% (full width at half maximum). The charge collection efficiency inside the diamond crystal was
0.4% (full width at half maximum). The charge collection efficiency inside the diamond crystal was  98% for both electrons and holes. The diamond detector also exhibited no significant degradation in terms of pulse height spectra and energy resolution during operation for more than 100 h in the case of mainly electron drift inside the diamond crystal. In contrast, the shapes of the pulse height spectra measured under hole drift condition deteriorated due to the polarization phenomenon.
98% for both electrons and holes. The diamond detector also exhibited no significant degradation in terms of pulse height spectra and energy resolution during operation for more than 100 h in the case of mainly electron drift inside the diamond crystal. In contrast, the shapes of the pulse height spectra measured under hole drift condition deteriorated due to the polarization phenomenon.
Mannan, M. A.*; Baba, Yuji; Kida, Tetsuya*; Nagano, Masamitsu*; Noguchi, Hideyuki*
Materials Sciences and Applications, 6(5), p.353 - 359, 2015/05
The synthesis and structure of hexagonal boron carbonitride (h-BCN) film on polycrystalline diamond surface were reported. Polycrystalline diamond and/or diamond-like carbon were first fabricated on Si (100) and then it was used as substrate. The deposition was performed by radio frequency plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. In order to reduce the content of nitrogen void defects, the deposition was performed at the high temperature of 950 C under the working pressure of 2.6 Pa. The typical sample with atomic composition of B
C under the working pressure of 2.6 Pa. The typical sample with atomic composition of B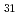 C
C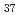 N
N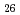 O
O in the h-BCN lattice was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The fine structure of the film was studied by near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) measurements. The B K-edge and N K-edge of NEXAFS spectra revealed that the synthesized h-BCN film has the ideal honeycomb-like BN
in the h-BCN lattice was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The fine structure of the film was studied by near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) measurements. The B K-edge and N K-edge of NEXAFS spectra revealed that the synthesized h-BCN film has the ideal honeycomb-like BN configuration without nitrogen void defects.
configuration without nitrogen void defects.
Okano, Fuminori; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Sakasai, Akira; Hanada, Masaya
Dai-27-Kai Genshiryoku Shisetsu Dekomisshoningu Gijutsu Koza Tekisuto, p.73 - 102, 2014/10
The disassembly of JT-60 tokamak device and its peripheral equipments, where the total weight was about 5400 tons, started in 2009 and accomplished in October 2012. This disassembly was required process for JT-60SA project, which is the Satellite Tokamak project under Japan-EU international corroboration to modify the JT-60 to the superconducting tokamak. This work was the first experience of disassembling a large radioactive fusion device based on Radiation Hazard Prevention Act in Japan. The cutting was one of the main problems in this disassembly, such as to cut the wielded parts together with toroidal field coils, and to cut the vacuum vessel into two. After solving these problems, the disassembly completed without disaster and accident.
Sakamoto, Keishi; Takahashi, Koji; Kasugai, Atsushi; Minami, Ryutaro; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Nishio, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Tobita, Kenji
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1263 - 1270, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:36.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Iihara, Junji*; Muramatsu, Yasuji; Takebe, Toshihiko*; Sawamura, Akitaka*; Namba, Akihiko*; Imai, Takahiro*; Denlinger, J. D.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 44(9A), p.6612 - 6617, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:43.27(Physics, Applied)Electronic structure transition between semiconducting and metallic states in boron (B) -doped diamonds was element-selectively observed by soft X-ray emission and absorption spectroscopy using synchrotron radiation. For the lightly B-doped diamonds, the B 2 -density of states (DOS) in the valence band were enhanced with a steep-edge-feature near the Fermi level, and localized acceptor levels, characteristic of semiconductors, were clearly observed both in B 2
-density of states (DOS) in the valence band were enhanced with a steep-edge-feature near the Fermi level, and localized acceptor levels, characteristic of semiconductors, were clearly observed both in B 2 - and C 2
- and C 2 -DOS in the conduction bands. For the heavily B-doped diamonds, the localized acceptor levels developed into extended energy levels and new energy levels were generated to form an extended conduction band structure which overlapped with the valence band. Thus, this clarified that the metallic energy band structure is actually formed by heavy boron doping. Such valence and conduction band structures observed by soft X-ray emission and absorption spectroscopy well accounted for the electrical properties of the B-doped diamonds.
-DOS in the conduction bands. For the heavily B-doped diamonds, the localized acceptor levels developed into extended energy levels and new energy levels were generated to form an extended conduction band structure which overlapped with the valence band. Thus, this clarified that the metallic energy band structure is actually formed by heavy boron doping. Such valence and conduction band structures observed by soft X-ray emission and absorption spectroscopy well accounted for the electrical properties of the B-doped diamonds.
Kusama, Yoshinori; Ishikawa, Masao
NEW DIAMOND, 21(3), p.24 - 25, 2005/07
no abstracts in English
Sudo, Tomoko*; Ohashi, Kazutoshi*; Sato, Toshimaro*; Ota, Eiji*; Okayasu, Satoru; Sugai, Hiroyuki
Physical Review B, 71(4), p.045211_1 - 045211_7, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.2(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have measured low frequency generation-recombination noise (g-r moise) spectra of a heavily boro-doped diamond crystal over the temperature range 20-300 K. The experimental results show that there are two peaks in the g-r noise spectrum at 120 K and 67 K, respectively. The 120 K peak corresponds to experimental evidence for the existence of hard gap having width of 10.4 meV. We interpret the 67 K peak as evidence for Wigner lattice formation whose gap width is 5.8 meV.
Ishikawa, Masao; Kusama, Yoshinori; Takechi, Manabu; Nishitani, Takeo; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Sasao, Mamiko*; Isobe, Mitsutaka*; Krasilnikov, A.*; Kaschuck, Y. A.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(10), p.3643 - 3645, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.7(Instruments & Instrumentation)Measurement of energy distribution of charge exchange neutral particles by using Natural Diamond Detector (NDD) has been started on the JT-60U Tokamak. Because the NDD is sensitive to neutrons and  -rays too, the radiation shield has been set up around the NDD. Then energy distribution of neutral particles corresponding to injected neutral beam energy are successfully obtained. Also, enhance of neutral particle flux due to sawtooth oscillation and Alfven Eigenmode induced by N-NBI was observed. The performance of the NDD as CX neutral particle analyzer under the DD neutron filed was demonstrated on JT-60U.
-rays too, the radiation shield has been set up around the NDD. Then energy distribution of neutral particles corresponding to injected neutral beam energy are successfully obtained. Also, enhance of neutral particle flux due to sawtooth oscillation and Alfven Eigenmode induced by N-NBI was observed. The performance of the NDD as CX neutral particle analyzer under the DD neutron filed was demonstrated on JT-60U.
Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Kaneko, Hiroshi*; Turkevich, V.*; Hamaya, Nozomu; Shimomura, Osamu*
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 31(4), p.261 - 268, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:41.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The graphite-diamond transformation was investigated by in situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction experiments using aqueous fluid containing dissolved MgO as the diamond forming catalyst under conditions of 6.6-8.9 GPa and 1400-1835  C. The transformed volume fractions of diamond as a function of time under various pressure-temperature conditions were obtained and analyzed using the JMAK rate equation. Variations in the nucleation and growth processes during diamond formation as a function of pressure and temperature were clarified.
C. The transformed volume fractions of diamond as a function of time under various pressure-temperature conditions were obtained and analyzed using the JMAK rate equation. Variations in the nucleation and growth processes during diamond formation as a function of pressure and temperature were clarified.
 X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperatures
X-ray diffraction of graphite-diamond transformation using various catalysts under high pressures and high temperaturesUtsumi, Wataru; Okada, Taku; Taniguchi, Takashi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kikegawa, Takumi*; Hamaya, Nozomu; Shimomura, Osamu
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(14), p.S1017 - S1026, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54(Physics, Condensed Matter)The graphite-diamond transformation was investigated using in-situ time-resolved X-ray diffraction experiments with a MgO dissolved aqueous fluid as the diamond forming catalyst under conditions of 6.6-8.8 GPa and 1400-1835 C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
C. Experiments were conducted using a 180-ton DIA-type cubic-anvil apparatus installed on the beamline BL14B1 at SPring-8, a third-generation synchrotron radiation facility in Japan. By analyzing the kinetic data using the JMAK rate equation, it was clarified that altering the pressure-temperature conditions drastically changes the nucleation and growth process of diamond.
Takahashi, Koji; Kasugai, Atsushi; Minami, Ryutaro; Sakamoto, Keishi; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Imai, Tsuyoshi
Denki Gakkai Genshiryoku Kenkyukai Shiryo (NE-03-1), p.1 - 6, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Kimura, Hiromi*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 66-68, p.651 - 656, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kajiwara, Ken; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kasugai, Atsushi; Seki, Masami; Moriyama, Shinichi; Takahashi, Koji; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 65(4), p.493 - 499, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:33.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Chiba, Shinichi; Inoue, Akira*
Proceedings of 30th EPS Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2003/00
It has been successful to apply CVD diamond plate as the vacuum window for infrared CO laser interferometry and polarimetry for electron density measurement in the JT-60U tokamak. In comparison with using the conventional zinc-selenide windows, the Faraday rotation component at diamond windows was small as negligible. This resulted in the improvement of the Faraday rotation measurement for a tokamak plasma by polarimetry.
laser interferometry and polarimetry for electron density measurement in the JT-60U tokamak. In comparison with using the conventional zinc-selenide windows, the Faraday rotation component at diamond windows was small as negligible. This resulted in the improvement of the Faraday rotation measurement for a tokamak plasma by polarimetry.
 X-ray observations of the diamond formation process in the C-H
X-ray observations of the diamond formation process in the C-H O-MgO system
O-MgO systemOkada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Shimomura, Osamu
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 14(44), p.11331 - 11335, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.6(Physics, Condensed Matter)In order to clarify the mechanism of diamond formation in the Earth's mantle, we studied the diamond formation in the H O-fluid by in situ X-ray observation with the simple C-H
O-fluid by in situ X-ray observation with the simple C-H O-MgO system. The results suggest that the solubility of MgO component increases greatly as a function of pressure. However, the generation of fluid is not a sufficient condition for diamond formation, because the carbon quantity in fluid is not increased drastically until just before the diamond formation temperature. This is the first report of the kinetics study in fluid using synchrotron radiation.
O-MgO system. The results suggest that the solubility of MgO component increases greatly as a function of pressure. However, the generation of fluid is not a sufficient condition for diamond formation, because the carbon quantity in fluid is not increased drastically until just before the diamond formation temperature. This is the first report of the kinetics study in fluid using synchrotron radiation.
Turkevich, V.*; Okada, Taku; Utsumi, Wataru; Garan, A.*
Diamond and Related Materials, 11(10), p.1769 - 1773, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:62.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Kasugai, Atsushi; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kajiwara, Ken*; Seki, Masami; Tsuneoka, Masaki*; Takahashi, Koji; Anno, Katsuto; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hiranai, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.435 - 451, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Katagiri, Masaki
Denki Gakkai Genshiryoku Kenkyukai Shiryo (NE-01-23), p.9 - 14, 2001/10
no abstracts in English